
- For Public
- For Patients
- Healthcare Professionals
- For Partners
- General Practitioners
- Community Partners
- Workplaces
- Schools
- Research & Innovation
- Careers
- Giving
- About Us
- I Want To
Overview
What is Tinea Pedis?

Tinea pedis (also known as "Athlete's foot") is a common fungal skin infection that affects the feet. It commonly affects the soles of the feet, arches and also between the toes.
Causes

1. Walking barefooted typically in communal areas

2. Repetitive use of soiled / wet footwear and socks
3. Spread of fungal infection from other parts of your body including toenails
4. Sharing of nail trimming tools, towels, socks, or shoes with a person who has fungal skin and / or toenail infection
Fungal foot skin infection may cause
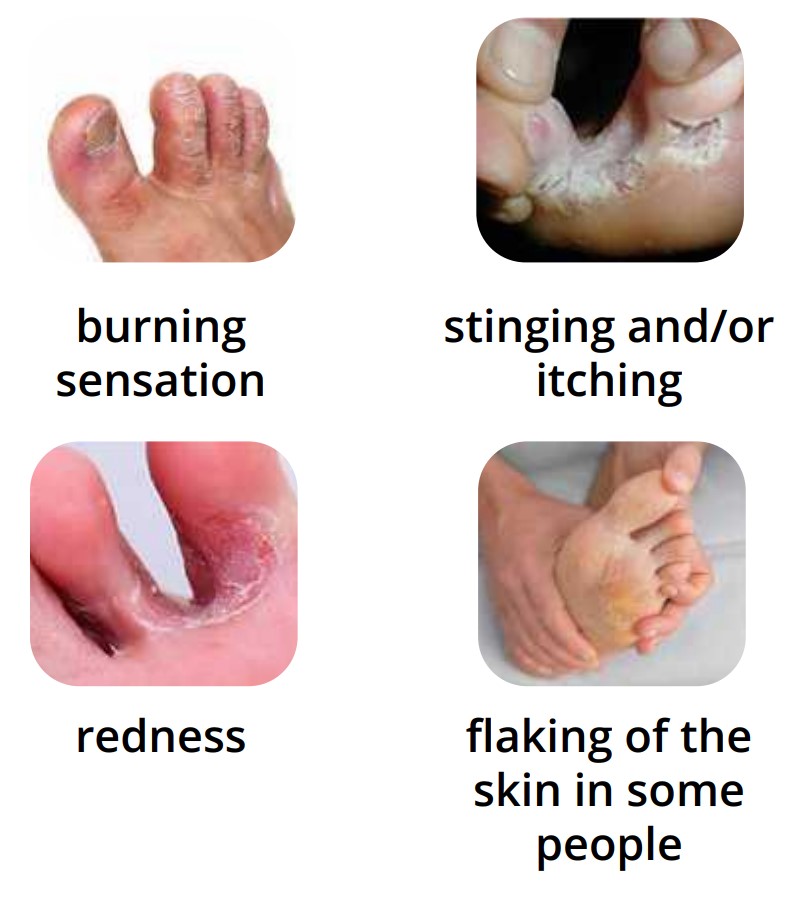
The infection can also affect the toenails
In people with neuropathy, there may be little or no symptoms
Prevention
What can I do to prevent getting fungal skin infection?:

Change socks daily or when wet (especially in people with excessive sweating).
Keep your feet clean and dry, especially between the toes, and before putting on your socks. Dab your feet dry especially in between your toes rather than rubbing them.
Use socks made from natural fibres e.g. cotton or absorbent material to improve wicking of sweat away from the body, especially if you have sweaty feet.

Use a separate towel for your feet and wash it regularly.

Wear protective footwear at communal or carpeted areas such as pools and hotel rooms.

Choose footwear made of breathable materials.

Have your diabetes under control to reduce the risk of developing fungal infection.
You can prevent its recurrence by the following measures:

Do not scratch affected skin. If you did touch the affected area, remember to wash your hands thoroughly as this can be spread from one part of your body or to another person by contact.

Do not share towels, socks, and shoes with another person.

Do air your shoes out regularly, especially if you work in a hot environment or have sweaty feet. In such cases, it will be recommended to alternate using different shoes.
Detection & Treatment
What are the treatments available?
Your doctor commonly prescribes antifungal cream (for areas affecting the top or bottom of the foot) or powder (for areas in between the toes). Apply anti-fungal cream on the affected areas 2-3 times a day for 4 weeks. You may consider purchasing these preparations such as antifungal cream or antifungal powder over the counter should you run out of supply.
If there are no improvement in two weeks, do consult your doctor for further assessment and treatment. Do not attempt to further self-medicate.
Do not stop using the medication even when the rash has cleared. Continue using it for at least 7 days after the infection appears to be cleared. In the case of white spots, the white colour remains even after the infection has been successfully treated. However, this will gradually improve over time as the skin regains its normal colour.
For prevention of white spots, use an antifungal shampoo once a month; on your scalp and body, leave it on for 10 minutes before washing it off. In the event of an infection, use this daily for 7 to 14 days consecutively.

In certain cases especially if topical treatment is ineffective, your doctor may send off skin scraping to check the type of fungal infection.
In severe cases, cases involving fungal toenail infection, cases not responsive to topical treatment, or infections affecting large areas, your doctor may prescribe oral antifungal medication. Fungal nail infection can be treated but often requires prolonged treatment. It is important to realise that eradication of the fungi does not guarantee that the nails return to a normal appearance.
Care Management
When should you seek medical treatment?

Specialties & Services