
- For Public
- For Patients
- Healthcare Professionals
- For Partners
- General Practitioners
- Community Partners
- Workplaces
- Schools
- Research & Innovation
- Careers
- Giving
- About Us
- I Want To
Overview
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammatory arthritis (warm, swollen, painful joints) and may affect other parts of the body including the eyes, lungs, skin, heart, blood vessels and nerves.
Can a Person With RA Become Pregnant or Have Children?
Yes, a person with RA can become pregnant or have his/her own child. However, as some medications taken may affect pregnancy, please discuss your family plans with your doctor. This also applies to male patients who are planning to start their own family.
What is the Outlook for Patients?
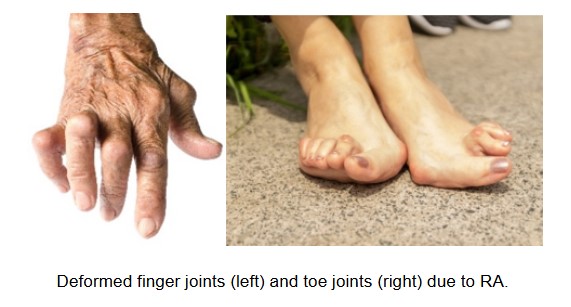
RA can be mild, moderate or severe. Majority of patients improves with treatment in the early stages of RA and lead normal lives. A small percentage of patients may have permanent joint damage and deformities. This may be due to unusually severe disease or negligence.
Causes
Who are at Risk of RA?
RA is more common in women. It usually occurs in people aged between 25 to 50 years old, but young children and elderly may be affected too.
What Causes RA?
The precise cause of RA is unknown. It is likely to be caused by a combination of factors like:
In early stages of RA, most people experience:
Overtime, the joints become warm, painful and swollen. The same joints on both sides of the body tend to be affected, especially the hands and feet.
People with RA may also:
Detection & Treatment
How is RA Diagnosed?
RA is diagnosed based on patient's medical history, physical examination and laboratory tests. Imaging may be required if RA is in its early stages or symptoms and signs appear unusual.
The doctor may also drain fluid from your joints to ensure your arthritis is not due to an infection or some other causes.
Your doctor may perform a biopsy to remove small bits of inflamed joint tissue or nodules for examination only when needed.
Common tests performed for RA patients include:
Early diagnosis can prevent irreversible joint damage and preserve joint function.
What are the Treatments for RA?
1. Patient Education
This consists of empowering yourself with knowledge and taking charge of your health.
Advice includes:

2. Medication
Majority of patients with RA require medications.
Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Usually used to reduce joint swelling, pain and stiffness.
Disease Modifying Anti-rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
Aims to suppress inflammation so that joint pain and swelling are controlled and damage to joints is minimised.
Corticosteroids)
Often used in low doses in combination with NSAIDs and DMARDs to enable quick control of inflammation.
3. Physiotherapy (PT) and Occupational Therapy (OT)
Improve pain control using non-pharmacological methods (e.g. heat and cold therapy).
Explore ways of improving mobility of injured joints and muscles (e.g. application of splints).
4. Biologic Agents
They are medical products extracted or produced from biological sources. They are expensive and reserved for arthritis that is not controlled by standard therapy.
5. Lifestyle Modification
Quit smoking, have adequate rest, exercise and maintain ideal body weight
Specialties & Services