
- For Public
- For Patients
- Healthcare Professionals
- For Partners
- General Practitioners
- Community Partners
- Workplaces
- Schools
- Research & Innovation
- Careers
- Giving
- About Us
- I Want To
Overview
What is Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)?
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) is a condition where an ulcer is created because of a break in the inside lining of your stomach or upper portion of your small intestine (duodenum).
Peptic ulcers that occur on the inside of your stomach are called gastric ulcers. If they occur on the inside of your duodenum, upper portion of your small intestine, they are called duodenal ulcers.
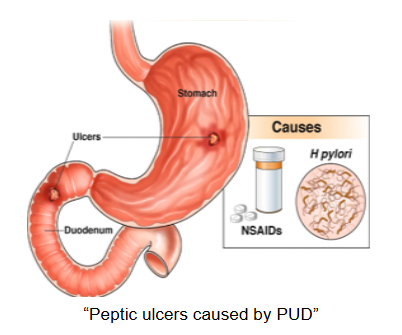
Causes
Two Major Causes of PUD:
1. Infection by bacteria Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)
The inner lining of the stomach or duodenum becomes swollen and painful after infection.
2. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
The lining of the stomach and duodenum become irritated after taking NSAIDs. These are pain medications, and common ones include naproxen, aspirin and ibuprofen.
What Can Increase Risk of PUD?
You may or may not experience the following:
Do note that the elderly commonly do not experience any symptoms.
Detection & Treatment
How Is PUD Diagnosed?
Some of the peptic ulcer symptoms may also be caused by other digestion-related conditions. Do see your doctor for advice.
You may be required to undergo some tests for confirmation, such as:
These test are generally safe and serious complications are rare.
What Are the Treatment Options?
Depending on the cause of the ulcers, treatments could be:
What Else Do I Need to Know?
Duodenal ulcers may cause abdominal pain several hours after eating (often during the night). This is because there is no food in the digestive tract for the stomach acid to work on.
Eating a meal, drinking milk or taking an antacid may help to relieve your symptoms.
If you are on NSAIDS, your doctor may recommend alternative medications.
If your ulcer was due to H. pylori, your doctor may do a urea breath test. This is to confirm that the infection is gone after a course of antibiotic medication.
Specialties & Services