Oropharyngeal Cancer
Overview
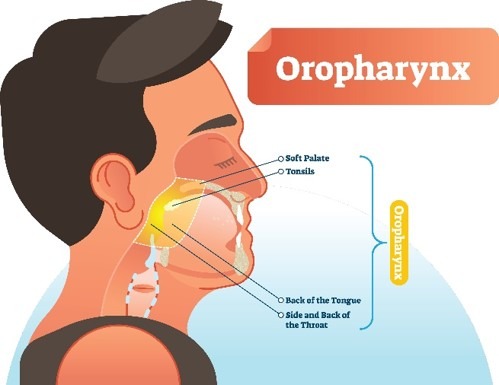
The oropharynx is the back of the throat that includes the back of the tongue, the tonsils and the soft palate with uvula.
Causes
- Smoking
- Execessive alcohol consumption
- There is association between Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) and oropharyngeal cancer with having previous multiple sexual partners and engaging in oral sex
Signs & Symptoms
- A lump at the back of the throat
- Difficulty or pain in swallowing
- Neck lumps due to enlarged lymph glands
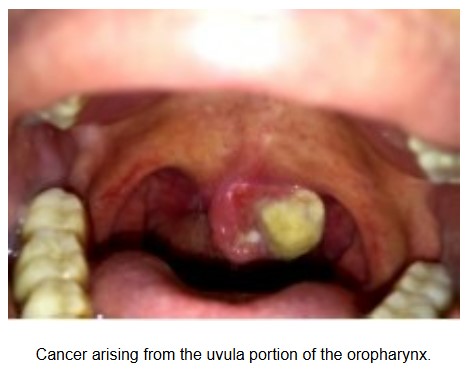
Detection & Treatment
Examination and Tests
Your doctor will perform a nasoendoscopy, where a fibreoptic camera is passed through your nose to obtain a view of the back of the tongue and throat.
Two types of investigations are required:
- Biopsy of the oropharynx to determine the presence of cancer. This is usually done under general anaesthesia.
- Scans to determine the spread of the disease. Commonly-performed scans include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan of the neck
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan of the whole body
Treatment
The treatment of oropharyngeal cancer depends on the stage of disease:
- Early stage: Either surgery OR radiotherapy
- Advanced stage: Surgery and chemoradiotherapy OR radiotherapy
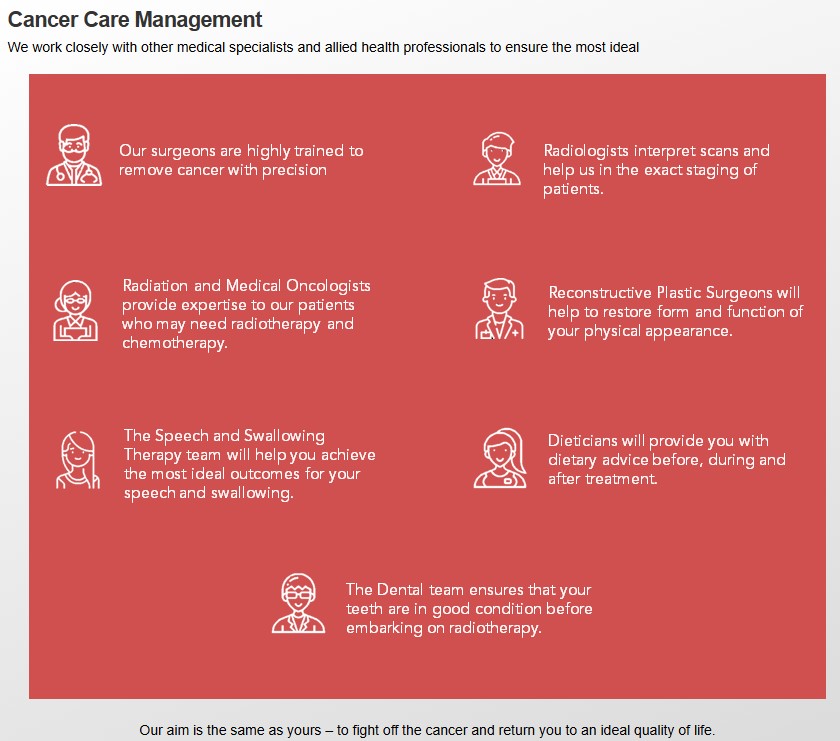
Care Management
Additional Resources
Specialties & Services

