
- For Public
- For Patients
- Healthcare Professionals
- For Partners
- General Practitioners
- Community Partners
- Workplaces
- Schools
- Research & Innovation
- Careers
- Giving
- About Us
- I Want To
Overview
What is Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease?
Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common viral illness that usually affects infants and children younger than five years old. It can sometimes occur in adults. It causes fever, blister-like sores in the mouth and or skin rash. It is caused by viruses that belong to the enterovirus genus group.
Causes
It is caused by viruses that belong to the enterovirus genus group.
How does HFMD spread?
The virus that causes HFMD can be found in an infected person's saliva, sputum, blister fluid, nasal mucus and faeces. HFMD virus spreads through:

Close personal contact.

Coughing or sneezing.
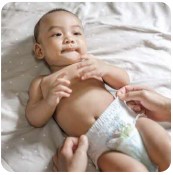
Contact with faeces (e.g. changing diaper of the baby with HFMD).

Touching contaminated objects and surfaces (e.g. toys, door knob) and then touching your eyes, mouth or nose.
HFMD usually begins with a fever, poor appetite, malaise (feeling unwell) and often with a sore throat.

One or two days after onset of fever, painful sores usually develop in the mouth. They begin as small red spots that blister and become ulcers, usually located on the tongue, gums and the inside of the cheeks.
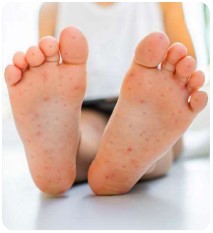
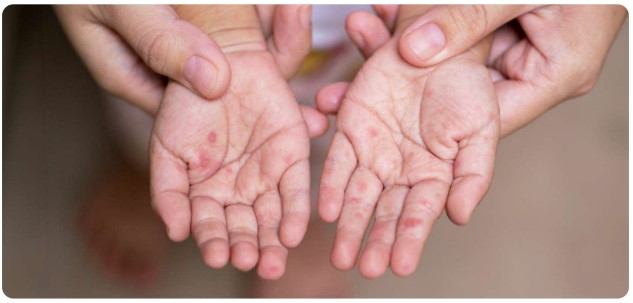
A non-itchy skin rash develops over one to two days. The rash has flat or raised red spots, sometimes with blisters.
The rash is usually located on the palms of hands and soles of the feet but may also appear on the buttocks and or genitalia. Sometimes, a person with HFMD may only have a rash or mouth sores.
Detection & Treatment
What can you do to prevent HFMD?
There is no specific treatment except to relieve pain and fever. There is also no vaccine available to protect against HFMD. However, the risk can be lowered if you:

Wash hands often with soap and water.

Clean and disinfect frequently touched surfaces and soiled items including toys.

AVOID close contact (e.g. kissing, hugging or sharing utensils or cups) with people who have HFMD.
Care Management
Infected persons are most contagious during the first week of illness. The viruses that cause HFMD can remain in the body for weeks after the symptoms have gone away. This means that the infected person can still pass the infection to other people even though he/she appears well. Also, some persons (including adults) who are infected and excreting the virus may have no symptoms. It is not transmitted to or from pets or other animals.

Specialties & Services