
- For Public
- For Patients
- Healthcare Professionals
- For Partners
- General Practitioners
- Community Partners
- Workplaces
- Schools
- Research & Innovation
- Careers
- Giving
- About Us
- I Want To
Overview
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs, but it can also occur in veins in other parts of the body.
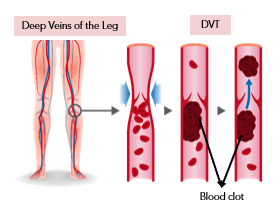
Causes
Blood clots in the veins can develop from:
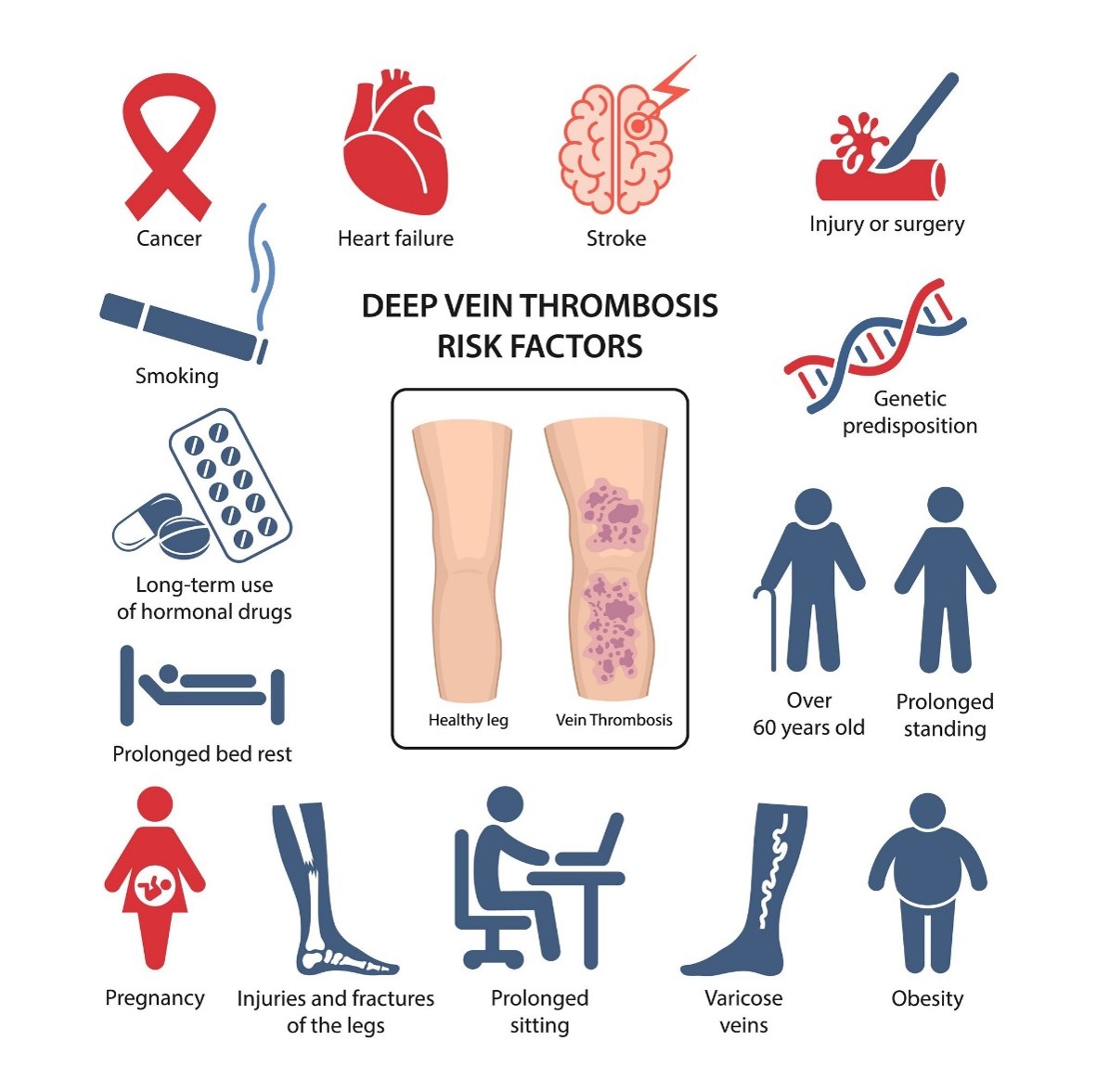
Who is at Risk of DVT?
DVT is more likely to occur in adults aged 60 years and older, but it can affect individuals of any age. Specific risk factors can increase the likelihood of the disease, which include the following:
Some people with DVT may not show any symptoms. Typical symptoms of DVT include:
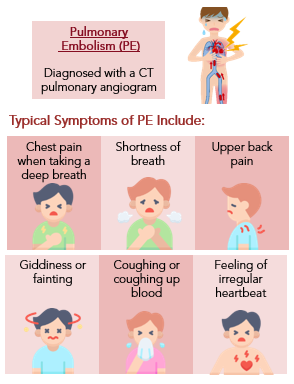
Dangers of DVT
While DVT is not immediately life-threatening, it can lead to serious complications:
Prevention
Detection & Treatment
How is DVT Diagnosed?
After a medical history and physical examination, your doctor might perform tests such as:
Treatment
Blood Thinning Medications (Anticoagulants)
Note: Follow your doctor's advice strictly, as these medications increase bleeding risk and need close monitoring.
Other Treatment Options
Your doctor may recommend the following treatments where necessary:
For Hospitalised Patients
Specialties & Services